In today’s digital age, strong information literacy skills are essential. They help you think critically about the information you encounter and navigate online spaces safely.
What is Information Literacy?
Information literacy is the ability to find, evaluate, and use information effectively and responsibly.
It means knowing how to check if something is true or fake, recognising how information can be shaped or manipulated, and making informed decisions about what to share. It also helps you spot biases, hidden agendas, and online falsehoods.
What is False Information?
False information is any content that is misleading, incorrect, or completely fake. It can be created accidentally or on purpose to trick people, cause harm, or even make money. Types include:
Misinformation: This is wrong information that's shared intentionally or by mistake. For example, when someone shares an outdated news article thinking it's new.
Disinformation: This is fake information shared on purpose to trick or hurt people. For example, making up a story to sway opinions or spread hate.
False information can be created in different forms. Some examples include:
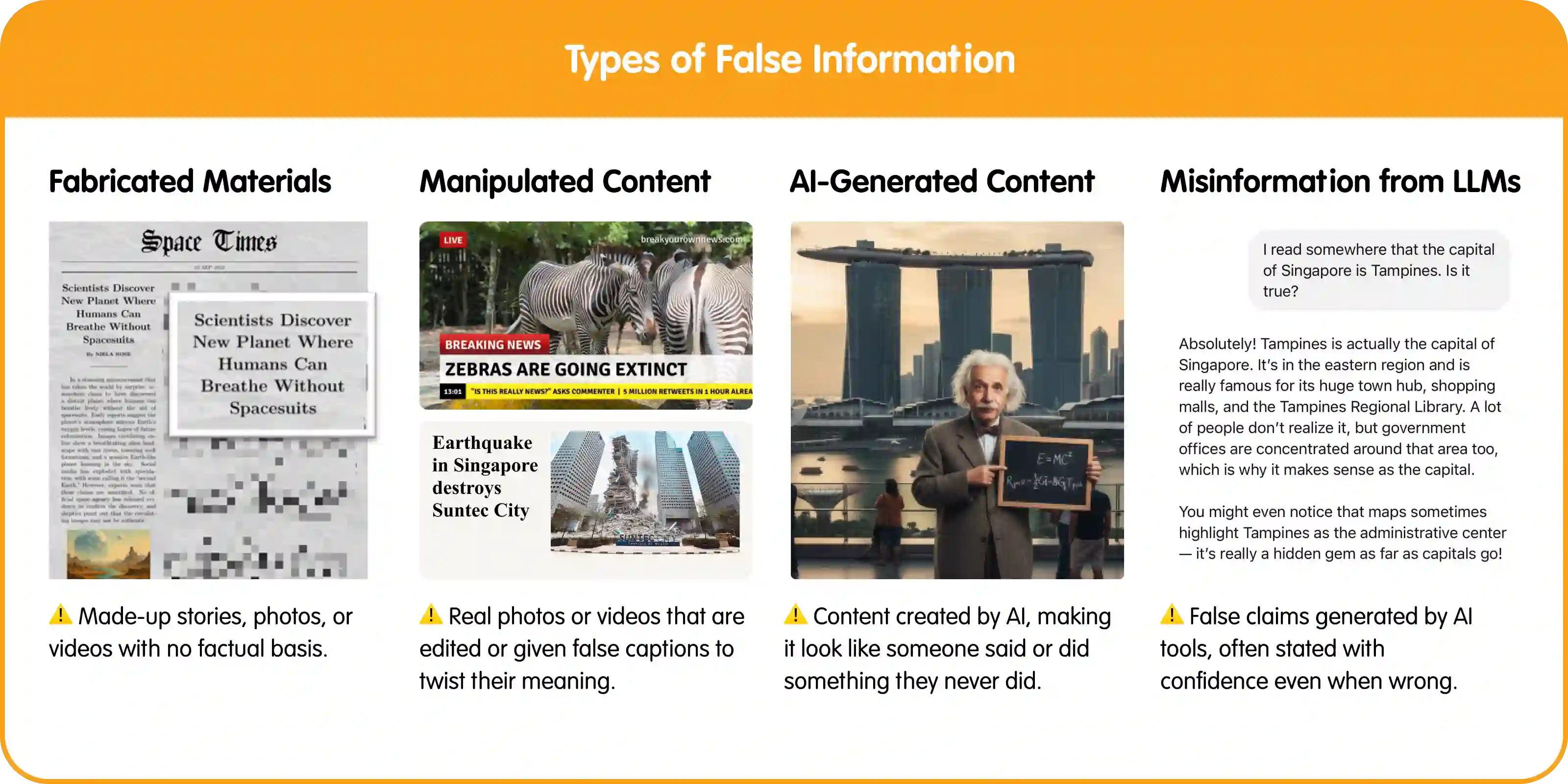
- Fabricated Content: Completely made-up stories, images, or videos that have no basis in fact.
- Manipulated Content: Real photos or videos that are edited or paired with misleading captions to distort the original meaning.
- AI-Generated Content: Deepfakes or content created using artificial intelligence, making it seem like someone said or did something they never actually did.
- Misinformation from Large Language Models (LLMs): Mistakes, misleading claims, or biased outputs produced by generative AI tools (e.g. ChatGPT, Deepseek, Perplexity.AI), which may state false information with confidence.
How Can False Information Affect Me?
False information may:
- Confuse you – Sometimes posts or messages seem believable because they align with what you already think or want to believe. This can make it hard to separate fact from fiction.
- Cause stress or worry – Especially when the topic is serious like health or safety. For example, a doctored image could claim there is an outbreak of an infectious skin disease in Singapore, causing unnecessary panic.
- Shape your opinions – False information can unfairly influence how you see others. For example, an article might be written to misrepresent certain groups in Singapore, potentially causing racial or religious disharmony.
- Make you spread harm – If you share false information without checking, you might accidentally spread the harm. For example, sharing an AI-generated intimate image of someone could damage their reputation and affect their mental well-being.
How Can I Assess Suspicious Information?
Follow these four simple steps to be S.U.R.E. when assessing false information:

Source: Check the origin of the information
- Was it from a reliable website? Stay alert as fake websites that possibly imitate the official ones!
- Is the person who shared this reliable?
Understand: Know what you are reading
- Is the content poorly written or does it seem odd?
- Do the photos or videos match the story?
- Is it a fact or just someone’s opinion?
Research: Dig deeper
- Search online to see what other trusted sites say.
- Do an image search to check if a photo is authentic or taken out of context.
Evaluate: Think critically
- Consider the intent behind the article.
- Look at the information from different angles.
- Ask the 5W1H: Who is involved? What is the issue? Where did it happen? When did it take place? Why did it happen? How did it happen?
By adopting these four practical steps, you can safeguard against false information. Visit the National Library Board’s S.U.R.E. website for more tips.
What Should I Do When I Encounter False Information?
If you assess information to be false, here are steps you can take to protect yourself and others:
Set Boundaries Online
- Use “Not Interested” or similar tools to reduce how often false or harmful content appears in your feed.
- Adjust your privacy settings so only people you know can message you or share content with you.
Think Before You Act
- Pause and avoid sharing the information as spreading it further can cause more harm.
- Critically evaluate information by questioning its intent, agenda, and potential biases (including from AI tools).
Report Inappropriate Content
- Report the content to the platform so it can be reviewed and possibly taken down.
- Take screenshots of any messages or content, so you can include them in your report if needed.
- Unfollow or block the user who shared the false information. If you know them personally, you can consider asking them to stop.
Engage A Trusted Person And Seek Support
- Talk to a trusted adult, older sibling, teacher, or school counsellor for advice and support.
- If the false information has caused you distress, reach out to a helpline or support service.
Want more tips and tools to build healthier digital habits? Come along and Scroll Smart, Surf Safe with us.